CRISPR Off-Target¶
Description¶
The image below shows a schematic of how OffTarget designs oligos in step-wise manner, walking away from a potential CRISPR off-target cut site; in this example the user has supplied an off-target site at the position chr6:56710100-56710101. The first oligo on either side is designed 10bp away from the cut-site, with adjacent oligos being designed a user-specified number of base-pairs (step size) further out, up until a specified maximum distance (m). Unlike the other pipelines, the intention is for only one oligo from each side of the off-target site to be used, based on the efficiency readouts shown in the output file oligo_info.txt (see Choosing Good Oligos for more information).
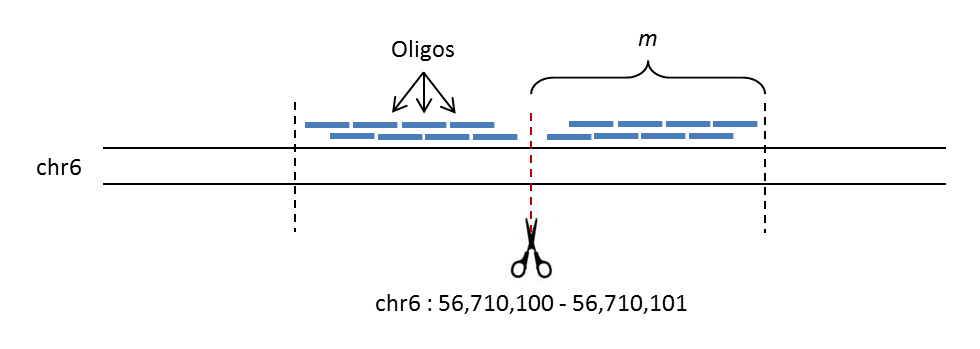
Schematic of oligo design by OffTarget¶
The unpredictability of indel mutations following CRISPR-mediated digestions should be taken into consideration since deletion of the expected oligo hybridisation region could occur. Moreover, oligos should not be designed too far away from the cut-site in order to maintain an efficient pull-down of the region. Due to these points, we recommend trying a few combinations of pairs at different distances, for optimisation.
Note
For full functionality, OffTarget should be run from the command line in order to test the efficiency of the generated oligos. This involves a pipeline that incorporates methods from the Tools class.
Usage¶
When run from the command line, oligo off-target takes the following parameters:
- -h, --help¶
(flag) Show this help message and exit
- -f <reference fasta>, --fasta <reference fasta>¶
(str) The path to the reference genome fasta
- -g <genome>, --genome <genome>¶
({mm9, mm10, hg18, hg19, hg38}) The name of the genome build
- -b <bed file>, --bed <bed file>¶
(str) The path to the bed file containing the coordinates of the expected CRISPR off-target cleavage sites
- -t <step size>, --step_size <step size>¶
(int, optional) The number of base-pairs between the start coordinates of adjacent oligos (see below), default=10
- -o <oligo length>, --oligo <oligo length>¶
(int, optional) The length (bp) of the oligos to design, default=70
- -m <maximum distance>, --max_dist <maximum distance>¶
(int, optional) The maximum distance away from the off-target site to design oligos to, default=200
- -s <STAR index>, --star_index <STAR index>¶
(str) The path to the STAR index directory; omit this option if running with BLAT (
--blat)
- --blat¶
(flag) Detect off-target binding using BLAT instead of STAR
Examples¶
Below are examples using the OffTarget pipeline for different scenarios
$ python -m oligo -cfg ./config.txt off-target -f ~/hg18/Sequence/genome.fa -g hg18 -b off_target_sites.bed -o 100 -t 50 -m 300 --blat
$ python -m oligo -cfg ./config.txt off-target -f ~/mm10/Sequence/genome.fa -g mm10 -b ms_off_targets.bed -o 50 -s ~/mm10/STAR/
API¶
As well as being run as a full pipeline from the command line, the design classes have been written such that the individual methods can be easily run in a python shell. The OffTarget pipeline implements methods from design.OffTarget. The following examples show the order in which the class methods are implemented:
>>> from oligo.design import OffTarget
>>> o = OffTarget(genome='hg19', fa='hg19_genome.fa', config_path="config.txt")
Loading reference fasta file...
...complete
>>> o.gen_oligos(bed='crispr_sites.bed', step=5, max_dist=150).write_oligos()
Generating oligos...
...complete.
Oligos stored in the oligo_seqs attribute
Wrote oligos to oligo_seqs.fa
>>> o.detect_repeats().align_to_genome(s_idx='/hg19/STAR')
Checking for repeat sequences in oligos, with RepeatMasker...
...complete. Output written to oligo_seqs.fa.out
Aligning oligos to the genome, with STAR...
...complete. Output written to oligos_Aligned.out.sam
>>> o.extract_repeats().calculate_density().write_oligo_info()
Repeat scores calculated
Density scores calculated
Oligo information written to oligo_info.txt
See design.OffTarget for more detailed information