Tiled Capture¶
Description¶
The image below shows a schematic of how Tiled designs oligos when run in either the default mode (top) or contiguous mode (bottom). In the top panel the user has run Tiled supplying the region chr10:13456000-13460000 and the restriction enzyme
DpnII. In the bottom panel the same coordinates have been used but with the --contig flag, and the step size set to equal the oligo length, thereby generating end-to-end oligos. For contiguous Tiled, the design is completely independent of
any restriction enzyme recognition sequences, however the DpnII sites have been left on the image for consistency.
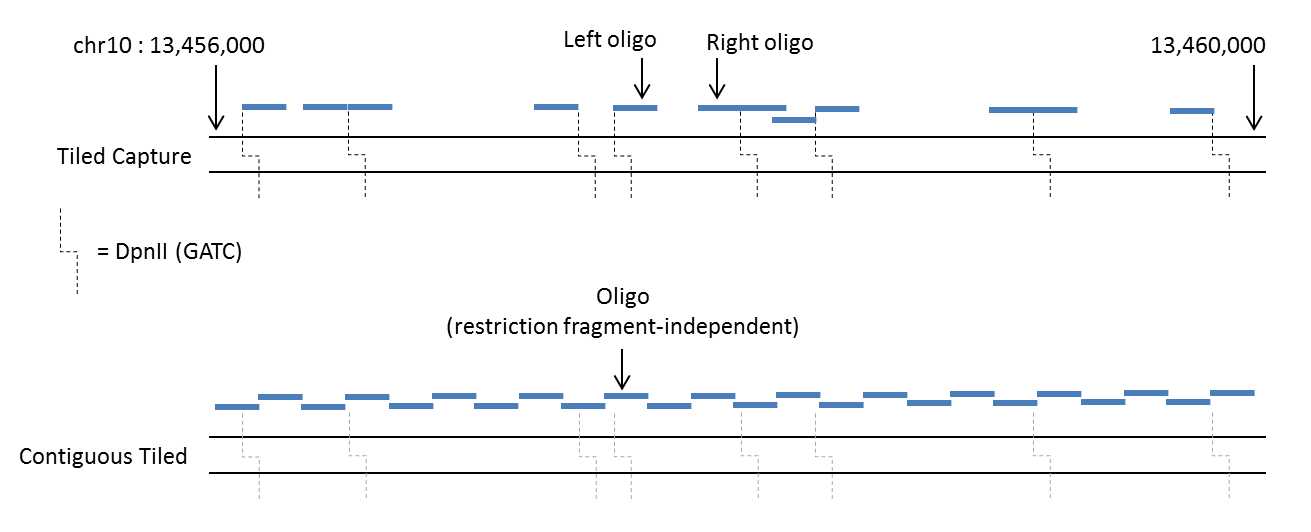
Schematic of oligo design by Tiled, in default (top) and contiguous (bottom) modes¶
It is possible for the Tiled Capture oligos to overlap, up to within 1bp of each other, when the restriction fragment is less than twice the length of the oligo. If the specified region consists of a fragment with length less than the specified oligo length, no oligos will be generated for that fragment. If the fragment length exactly equals the oligo length, only one oligo will be generated. Similarly, in contiguous Tiled, oligos can be designed such that they overlap up to within 1bp of each other; in this case, the step size would be set to 1.
Note
For full functionality, Tiled should be run from the command line in order to test the efficiency of the generated oligos. This involves a pipeline that incorporates methods from the Tools class.
Usage¶
When run from the command line, oligo tiled takes the following parameters
- -h, --help¶
(flag) Show this help message and exit
- --contig¶
(flag) Run the pipeline in contiguous mode
- -f <reference fasta>, --fasta <reference fasta>¶
(str) The path to the reference genome fasta
- -g <genome>, --genome <genome>¶
({mm9, mm10, hg18, hg19, hg38}) The name of the genome build
- -c <chromsome>, --chr <chromosome>¶
(str) The number/letter of the chromosome on which to design oligos e.g. 7 or X
- -r <region>, --region <region>¶
(str, optional) The region in which to design the oligos; must be in the format ‘start-stop’ e.g. 10000-20000; omit this option to design oligos across the entire chromosome
- -e <enzyme>, --enzyme <enzyme>¶
({DpnII, NlaIII, HindIII}, optional) Name of the restriction enzyme to be used for fragment digestion, default=DpnII; omit this option if running in contiguous mode (
--contig)
- -o <oligo length>, --oligo <oligo length>¶
(int, optional) The length (bp) of the oligos to design, default=70
- -t <step size>, --step_size <step size>¶
(int, optional) The number of base-pairs between the start coordinates of adjacent oligos (see below), when running in contiguous mode (
--contig), default=70; omit this option if you are not using the--contigflag
- -s <STAR index>, --star_index <STAR index>¶
(str) The path to the STAR index directory; omit this option if running with BLAT (
--blat)
- --blat¶
(flag) Detect off-target binding using BLAT instead of STAR
Examples¶
Below are examples using the Tiled pipeline for different scenarios
$ python -m oligo -cfg ./config.txt tiled -f ~/hg38/Sequence/genome.fa -g hg38 -c 18 -o 120 -s ~/hg38/STAR/
$ python -m oligo -cfg ./config.txt tiled --contig -f ~/mm9/Sequence/genome.fa -g mm9 -c X -r 10150000-10200000 -o 50 -t 60 --blat
Specifics¶
- Contiguous mode (
--contig) Running the pipeline in contiguous mode no longer restricts oligo design to Capture-C specification and hence the oligos are designed independently of any restriction fragment or recognition sequence. Instead, the user defines a step size (
-t,--step_size) to design oligos within close proximity to each other, across a specified region (-r,--region) or entire chromosome
- Restriction enzyme (
-e,--enzyme) The restriction enzyme being used in the Tiled Capture experiment (if not running in contiguous mode). This determines the recogition sequence used to define the fragment boundaries and hence the starts and ends of the oligos. The current version supports DpnII (GATC), NlaIII (CATG) and HindIII (AAGCTT). If this option is omitted, DpnII will be used by default.
- Step size (
-t,--step_size) The step size option allows for overlapping oligos to be designed, if required. A step size of 1 for 70bp oligos will shift the next oligo just 1bp to the right so that two adjacent oligos will overlap by 69bp. To design exact end-to-end oligos, the step size must equal the oligo length (
-o,--oligo)
- STAR (
-s,--star_index) or BLAT (--blat) To check for off-target binding, either the sequence aligner STAR or the BLAST-like Alignment Tool (BLAT) can be used. By default, STAR is used, unless design.py Tiled is run with the
--blatflag. Since BLAT is more widely used to detect off-target binding events, this might be preferred by the user. However, BLAT can be particulary slow for large designs, especially for the human reference genomes. STAR’s exceptional speed is better suited for designs with >1000 oligos. If the--blatflag is not selected, the path to the STAR index must be supplied after the-s(or--star_index) flag.
API¶
As well as being run as a full pipeline from the command line, the design classes have been written such that the individual methods can be easily run in a python shell. The Tiled pipeline implements methods from design.Tiled. The following examples show the order in which the class methods are implemented:
>>> from oligo.design import Tiled
>>> t = Tiled(genome='hg38', fa='hg38_genome.fa', config_path="config.txt", blat=True)
Loading reference fasta file...
...complete
>>> t.gen_oligos_capture(chrom=7, region='100000-120000', enzyme='NlaIII').write_oligos()
Generating oligos...
...complete.
Oligos stored in the oligo_seqs attribute
Wrote oligos to oligo_seqs.fa
>>> t.detect_repeats().align_to_genome()
Checking for repeat sequences in oligos, with RepeatMasker...
...complete. Output written to oligo_seqs.fa.out
Aligning oligos to the genome, with BLAT...
...complete. Output written to blat_out.psl
>>> t.extract_repeats().calculate_density().write_oligo_info()
Repeat scores calculated
Density scores calculated
Oligo information written to oligo_info.txt
See design.Tiled for more detailed information